Global companies, such as GE and Ipsen, see business expand rapidly in country's market
GE Healthcare has sold 100 of its new optical magnetic resonance machines in China over the past nine months and 500 across the globe during the past two years.
|
 |
|
A salesman shows a computer tomography machine at the 20th China International Medical Equipment & Affiliated Facilities Exhibition and Scientific Conference. Many international medical-care companies, including drugmakers and medical-device producers, have begun conducting research and development in emerging markets such as China. [Photo/China Daily] |
These are strong sales figures, but perhaps more striking is the fact that the machine is both manufactured and developed in China.
China contains an important part of the company's international research and development capabilities and has been integral in its global business model for some years, according to Richard Hausmann, vice-president of magnetic resonance healthcare systems at GE Healthcare, the medical arm of General Electric Co.
GE Healthcare is not alone. Many international medical care companies, including drug makers and medical device producers, have begun conducting R&D activity in emerging markets such as China, before using the advances made to extend their power in global market.
"We intend to significantly strengthen our engineering capabilities in China and will more than double our engineering workforce just for magnetic resonance," said Hausmann.
GE Healthcare plans to have 180 magnetic resonance engineers in China by the end of the year, compared to 20 it had when its China R&D center was set up in Beijing in 2007.
GE's new magnetic resonance machines are now exported to Japan, India, South America and Europe. Over the next three years the company will speed up R&D activity, manufacturing and training in order to increase production. It will also further localize raw material and component supplies to strengthen price competitiveness and enhance its installation and maintenance services, said Hausmann.
International drug maker Ipsen has not followed the GE route. Instead of setting up an R&D facility in China, it is in search of local research institutes and universities to cooperate with.
According to Marc de Garidel, chairman and chief executive officer of the France-based company, Ipsen's strategy in China includes opening an office in Beijing to cover its Asia business, an operations center engaged in collaborations with local institutes and the expansion of clinical experiments in China.
Ipsen, with sales at 1.1 billion euros ($1.42 billion) last year, primarily develops and markets medications used in oncology, endocrinology and the treatment of neuromuscular disorders. It spends 23 percent of its sales every year on R&D.
"We are a medium-sized company. We are prudent and prefer to cooperate with local partners," said Garidel. "In addition to clinical experiments, we will do more early-stage R&D in China with our partners for both the Chinese market and also our business globally."
According to Zhang Guang, an analyst at Forward Business Intelligence Co Ltd, the local collaboration model is a cost-effective and flexible alternative for companies without huge capital support.
"Chinese medical institutes receive national support with R&D and universities are good at early-stage discovery," she added.
Ipsen has been active in organizing professional exchange activities in China and in September held a forum in Beijing. Garidel said that Ipsen wants to create a platform for domestic and international officials, scholars and businesses to communicate and exchange scientific achievements.
Such activities are also an opportunity for the French company to promote its new products and technologies to both the Chinese market and international arena.
Inventor of insulin and currently the world's biggest producer Novo Nordisk officially launched its largest overseas R&D center in Beijing on Sept 25. With investment of more than $100 million, the Danish company hopes the facility can support scientific research into new products and technology that will be used around the world.
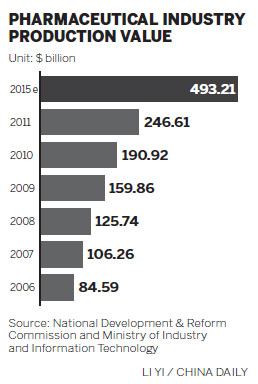
Zhang said that sluggish economic conditions and medical cost pressures in developed economies are stimulating the need for cheaper high quality development and production of medications and medical equipment. Emerging markets are also beginning to feel cost pressures. This is likely to fuel the need for more R&D activity in emerging markets, where costs are lower.
Emerging markets too are becoming an increasing source of demand. GE Healthcare has seen double-digit annual growth in its business in China for several years, considerably higher than its global performance. And Ipsen has seen rapid growth in its China sales, up 15 percent year-on-year compared to 5 percent in Europe.
liujie@chinadaily.com.cn
