'Super diamond' from graphite created

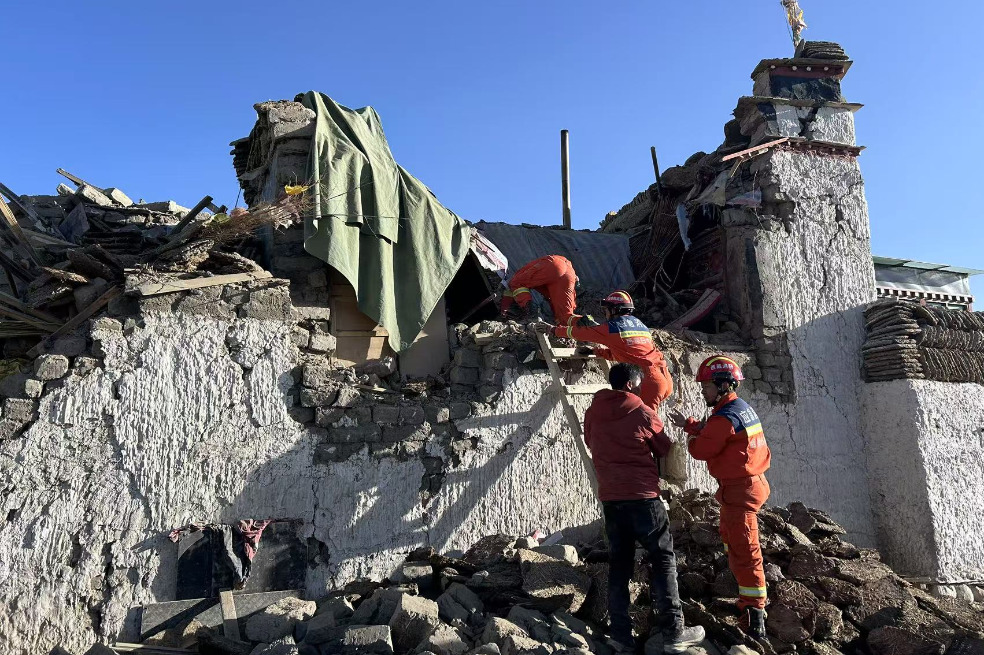
Chinese scientists have synthesized a "super diamond" that is 40 percent harder than natural diamonds and exhibits high thermal stability, a breakthrough that could enhance the performance of semiconductor materials in the future.
A joint team from Jilin University and Sun Yat-sen University announced the discovery on Feb 10, saying they successfully synthesized millimetersized lonsdaleite from graphite under extreme heat and pressure.
Lonsdaleite, also known as the meteoric diamond, was first discovered in 1967 and is formed from the impact of a meteorite hitting Earth's surface. Previously, lonsdaleite had only been found at meteorite sites.
"Due to its hardness, thermal stability and other properties, lonsdaleite can compensate for the performance limitations of natural diamonds in certain applications," said Yao Mingguang, a professor at the State Key Laboratory of Superhard Materials at Jilin University. "The synthesis of lonsdaleite has been a focal point of research for scientists worldwide for the past 50 years."
The United States, Japan and other nations have previously attempted to synthesize meteoric diamonds, but due to limitations in preparation methods, past results were low in purity and remained at the nanoscale.
The hexagonal diamonds synthesized by the Chinese team have made breakthroughs in both size and purity, Yao said. The process required pressure 300,000 times that of Earth's atmosphere — six times the pressure needed for synthetic diamonds, which are typically produced under 50,000 atmospheres. The resulting lonsdaleite crystals measure 1.2 millimeters in diameter.
The newly synthesized diamonds exhibit thermal stability and remain stable at temperatures up to 1,100 C, Yao said. They are also direct bandgap semiconductors with a bandgap 20 percent smaller than that of natural diamonds, suggesting potential advantages in semiconductor applications.
In semiconductor materials, the bandgap determines conductivity. A smaller bandgap generally indicates better conductivity, while a larger bandgap often signifies the material functions as an insulator or semiconductor.
Currently, lonsdaleite synthesis remains in the experimental stage, and further research is needed to transition from laboratory production to large-scale manufacturing, Yao said.
"Finding suitable catalysts may pave the way for industrial-scale production," he said.