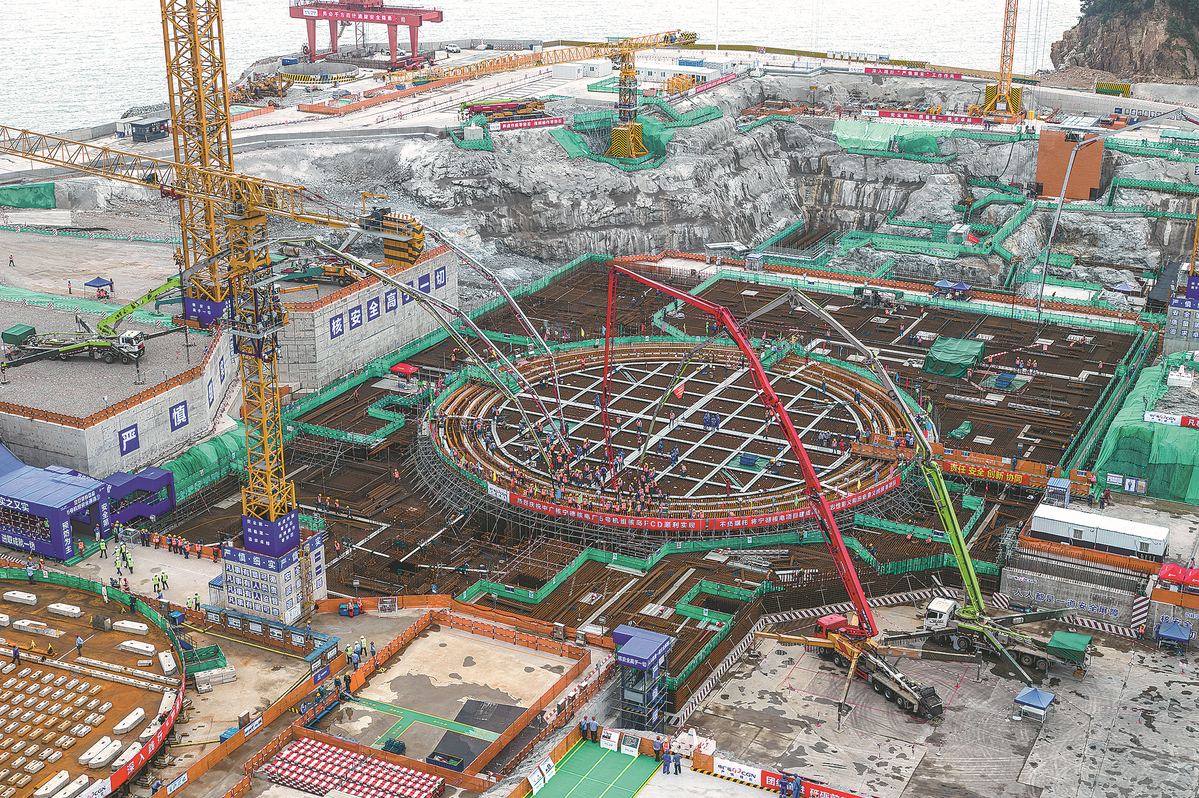
Nuclear power key to sustainable, greener energy
In past 10 years, nation adds 37 reactors, bringing total to 55, says IAEA


For decades, China relied heavily on imports to secure the uranium needed to fuel its nuclear reactors. However, the country has taken steps to diversify and secure its uranium supply.
Chinese companies have invested in uranium mining operations in countries such as Kazakhstan to ensure a stable and reliable fuel supply for its reactors.
In addition to securing overseas uranium supplies, China is also investing in domestic mining projects. The country is exploring new methods of extracting uranium and is developing technologies to recycle nuclear fuel, reducing its reliance on imported uranium over the long term.
According to China Nuclear Uranium Co Ltd, uranium exploration and development efficiency in China has significantly increased over the past few years, with the incremental resource amount in the past 10 years accounting for one-third of China's total confirmed reserves.
The country's natural uranium sector, covering geological exploration, mining, refining and processing, has developed into a complete industry chain over the decades. It has established a natural uranium supply system that combines domestic development, overseas growth, international trade and strategic reserves, it said.
Ensuring sufficient supplies of uranium and strengthening energy security will help China reduce dependency on foreign resources while mitigating geopolitical risks, said Zhao Xiangbin, chief strategist at Beijing Gold and Forex Fortune Investment Management.
As the country's nuclear power resources expand, ensuring a steady and affordable supply of uranium will be key to maintaining energy security and avoiding disruptions in its nuclear power generation capacity, he said.
Looking to the future, China is set to continue its rapid nuclear expansion, which is expected to account for 10 percent of China's total power output in 2035, up from 5 percent in 2021 and equivalent to reducing 900 million metric tons of carbon dioxide, said the China Nuclear Energy Association.
China's energy policy is leaning toward strong growth in nuclear, which is seen as a carbon-free low-cost alternative in the country's energy transition, said S&P Global Commodity Insights.
As China continues to develop its nuclear power sector, the country is poised to play a pivotal role in the global nuclear energy market, both as a producer of electricity and as a supplier of nuclear technology, said Lin.
"As the world's largest energy consumer and emitter, China's success in scaling up its nuclear sector could serve as a model for other nations seeking to balance energy security with sustainability."